OVERVIEW:
In this session, we'll learn about what business operations are and why they're important for your small business. By understanding these basics, you can keep your business running smoothly and efficiently.
- What Business Operations Includes
- Overview of Business Operations
- Key Components of Business Operations
- How Business Operations Impact Profitability and Success
- Alignment with Business Objectives
- Operational Efficiency and Profitability
- Operations and the Production and/or Sourcing Process
- Designing the Production Process
- Sourcing Materials and Services
- Ethics and Sustainability
- The Supply Chain and How to Manage It
- Operations for Sales and Marketing
- Pricing, Costs, and Operational Efficiency
- Factors Influencing Pricing
- Pricing Strategies: Exploring Diverse Approaches
- Managing Operational Costs
- Efficiency and Quality in Business Operations
- Top 10 Do's and Don'ts
- Business Resources
Watch this session in Video Format (42:17)
In this session, we'll learn what business operations are and why they're important for your small business. By understanding these basics, you can keep your business running smoothly and efficiently.
Overview of Business Operations
Definition and Scope
Business operations are the everyday activities that keep your business going. This includes making products or offering services, managing supplies, marketing your business, and helping your customers. No matter the size of your business, the main goal of operations is to create and deliver value in the best way possible.
Operations Role in Business Structure
In a small business, operations are key to everything. They connect different parts of your business together, making sure everyone works towards the same goals. Good operations management helps you use your resources wisely and meet your business goals.
Getting Started with Operations
Creating operations for your business can seem like a major undertaking, and it can be difficult to know where to start. One of the best ways to begin to create an operations plan, for any area of your business, is to document your steps. The steps you take to create and deliver your product, to provide your service, to order your supplies, to schedule and invoice your customers, these are all examples of processes you follow in your business.
By documenting your processes, you can see how you operate your business. This is the foundation for your operations plan. By reviewing the things you are doing, you can begin to look for areas of improvement, ways to do things better, faster, with better quality, with less waste, etc. and build your plans around achieving these objectives and your business goals.
Key Components of Business Operations
- Production or Service Delivery:
This is about making your products or providing your services. For product-based businesses, it means getting materials, making products, and checking quality. For service-based businesses, it’s about planning and delivering services to satisfy customers.
- Supply Chain Management:
Supply chain management is about handling the flow of goods and information from suppliers to customers. This includes getting materials, managing stock, and making sure products or services are delivered on time. Good supply chain management helps cut costs, maintain a consistent and predictable schedule, and keep customers happy.
- Sales and Marketing:
Sales and marketing are about attracting and keeping customers. This includes market research, marketing, advertising, sales tactics, and engaging with customers. Effective sales and marketing help your business grow by bringing in more customers and increasing sales.
- Customer Service:
Great customer service ensures your customers are happy and come back again. This means providing information, answering questions, solving problems, and building good relationships with customers. Excellent customer service sets your business apart from others and builds customer loyalty.
- Information Technology:
Information technology (IT) supports all parts of your business. This includes using software for scheduling, accounting, human resources (if you have employees), managing customer relationships, tracking inventory, and more. IT helps automate tasks, improve communication, and boost productivity.
- Quality Control and Efficiency:
Quality control means making sure your products or services always meet certain standards. Efficiency is about making your processes better to save time and reduce waste. Together, they help you provide high-quality products or services at a lower cost.
Integration of Operations Across the Business
Teamwork helps everyone work towards common goals and makes your business run better. Operations are a big part of planning your business’s future. By knowing what your operations can and can’t do, you can set realistic goals and make plans to reach them. Operations help you carry out these plans and achieve your long-term business goals.
By understanding the basics of business operations, you can manage your small business better, improve efficiency, and reach your goals. In the next sections, we'll look at each part in more detail and give you practical tips and strategies for success.
Importance of Efficient Operations in Achieving Business Objectives
In this section, we’ll discuss why efficient operations are essential for reaching your business goals. We’ll explore the connection between operations and profit, how operations align with business objectives, and provide examples from different industries. We'll also look at how operational efficiency can boost profit margins through cost reduction, share case studies, and highlight how good operations can give you a competitive advantage through innovation and quality.
Link Between Operations and Profit
Efficient operations are vital because they help you maximize your profits. When your business processes are streamlined, you can produce goods or provide services more quickly, with greater consistency, and at a lower cost. This means you can serve more customers without increasing your expenses, leading to higher profits. For instance, if you find a way to reduce the time it takes to produce a product, you can make more products in the same amount of time, thus increasing your sales and profits.
Alignment with Business Objectives
- Role of Operations in Achieving Business Goals:
Operations are the backbone of your business plans. They turn your strategies into actions. If your goal is to provide fast delivery, your operations should be designed to support that, such as by optimizing your logistics and supply chain. Each aspect of your operations should help achieve your business objectives, ensuring that your daily activities contribute to your long-term goals.
- Examples from Different Industries:
- Retail: Efficient operations in retail might focus on inventory management to ensure products are always available without overstocking. Streamlined checkout processes can also enhance customer satisfaction and speed.
- Restaurants: In the food industry, efficient operations might mean quick food preparation and excellent customer service to ensure diners are happy and return for future meals
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, operations might focus on reducing production time and minimizing waste, leading to higher output and lower costs.
Operational Efficiency and Profitability
- Cost Reduction and Profitability:
Efficient operations help reduce costs, which directly impacts your profit margins (the percentage of revenue that remains after you subtract all costs associated with your product or service). By optimizing processes and eliminating waste, you can increase your profit margin, to have more money that can be reinvested in your business or added to your profits. For example, automating repetitive tasks can save costs and reduce errors, leading to cost savings and higher profitability.
- Competitive Advantage:
- Innovation in Operations:
- Innovation in operations can set your business apart from the competition. By finding new and better ways to do things, you can offer unique products or services, or deliver them more efficiently. This might involve adopting new technologies, improving processes, or finding creative solutions to common problems. Innovative operations can help you stay ahead in the market.
- Quality as a Differentiator:
- High-quality operations ensure that your products or services consistently meet or exceed customer expectations. Quality control processes help maintain standards and prevent mistakes, which can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. When customers know they can rely on your business for quality, they are more likely to choose you over competitors.
By focusing on efficient operations, you can improve profitability, align your actions with business goals, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge through innovation and quality. In the next sections, we’ll dive deeper into specific strategies and tools you can use to enhance your operations.
In this section, we'll explore how to design effective production processes, source materials and services, and ensure ethical and sustainable practices. Whether you’re making products or delivering services, understanding these aspects will help you create high-quality offerings and maintain strong relationships with suppliers while promoting responsible business practices.
Designing the Production Process
- Product Design and Development:
Product design and development are the first steps in creating a product. Start by identifying what your customers need and want. Use this information to create a product that solves a problem or fulfills a desire. During development, focus on making your product easy to use, reliable, and cost-effective to produce. Testing prototypes and getting feedback from potential users can help you refine your design.
- Manufacturing Processes:
Once you have a final product design, the next step is to set up your manufacturing process. This involves determining how your product will be made, what equipment and materials you’ll need, and how to organize the workflow. Aim for a process that is efficient and minimizes waste. Document each step and ensure that all employees are trained to follow the procedures correctly to maintain consistent quality.
Sourcing Materials and Services
- Criteria for Selecting Suppliers:
Choosing the right suppliers is crucial for your business. Look for suppliers who offer high-quality materials or services at a reasonable price. Reliability is also important; your suppliers should be able to deliver on time and meet your specifications. Some suppliers may only work with established businesses, or they may have order minimums. Evaluate potential suppliers based on their reputation, financial stability, and willingness to collaborate on solving problems. You may even be able to find a local supplier who is enthusiastic about supporting another business in the community.
- Managing Supplier Relationships:
Building strong relationships with your suppliers can lead to better deals and more reliable service. Communicate clearly and regularly with your suppliers about your needs and expectations. Treat them as partners in your business, and work together to address any issues that arise. Maintaining good relationships can help you negotiate better terms and ensure a steady supply of materials.
Ethics and Sustainability
- Responsible Sourcing Practices:
Responsible sourcing means choosing suppliers who adhere to ethical standards. This includes fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and environmentally friendly operations. By selecting ethical suppliers, you support good practices and reduce the risk of scandals that could damage your reputation.
- Impact of Sustainability on Brand Image and Costs:
Sustainable practices can enhance your brand image and attract customers who value environmental responsibility. While some sustainable materials and processes might be more expensive upfront, they can save money in the long run through efficiency gains and reduced waste. Additionally, promoting your commitment to sustainability can differentiate your brand and build customer loyalty.
By carefully designing your production processes, choosing and managing suppliers wisely, and committing to ethical and sustainable practices, you can create high-quality products that meet customer expectations and build a strong, reputable brand. In the following sections, we will continue to explore other key aspects of business operations that contribute to the success of your small business.
In this section, we’ll dive into the essentials of supply chain management. You’ll learn what a supply chain is, why it’s important, and how to manage it effectively. We’ll cover the basics of supply chains, how to design a good supply chain strategy, and ways to manage risks to keep your supply chain resilient.
Fundamentals of Supply Chain Management
- Definition and Importance of Supply Chain Management:
A supply chain is a network of all the people, organizations, and activities involved in creating and delivering a product or service to the customer. This includes everything from getting raw materials to producing goods and delivering them to the end user. Supply chain management involves coordinating and overseeing these activities to ensure everything runs smoothly and efficiently.
Effective supply chain management is crucial because it helps reduce costs, improve efficiency, and ensure that products are available when customers need them. By managing your supply chain well, you can meet customer demands, reduce delays, and increase your overall competitiveness.
- Key Elements of Supply Chains:
In a typical product-based business, your supply chain might include these parts:
-
- Suppliers: Provide the raw materials or components needed to create your products.
- Manufacturers: Convert raw materials into finished products.
- Distributors: Store and transport products to retailers or customers.
- Retailers: Sell the final product to customers.
- Customers: The end users who purchase and use your products.
In a service-based business, like a mobile car wash, dog walking service, or website design, your supply chain might include these parts:
-
- Suppliers: The entity providing the service (perhaps you and/or your team).
- Supporting Infrastructure: The tools, equipment, and resources necessary for you to deliver your service effectively.
- Business Operations: Administrative tasks and processes you need to deliver the service, like scheduling, billing, and customer support.
- Marketing and Promotion: Activities and strategies to attract and retain customers.
- Customers: The end users who purchase your service.
Supply Chain Strategy
- Designing an Effective Supply Chain:
To design an effective supply chain, start by understanding your customers' needs and your business goals. Map out the entire supply chain from suppliers to customers, and identify key areas for improvement. Focus on creating a supply chain that is efficient, flexible, and capable of responding quickly to changes in demand.
Consider factors like location of suppliers, transportation methods, inventory levels, and production schedules. Use these insights to create a strategy that minimizes costs while maximizing speed and reliability.
- Technology’s Role in Supply Chain Optimization:
Technology can play a vital role in optimizing supply chains. Today’s supply chain management software can be used to track inventory levels, manage orders, and monitor deliveries in real-time. Using technology to add automation in these areas can help streamline processes and reduce errors.
Risk Management in Supply Chains
- Identifying and Minimizing Risks:
Supply chains can be vulnerable to various risks, such as supplier failures, transportation delays, natural disasters, and economic changes. To manage these risks, start by identifying potential threats to your supply chain. This can include evaluating your suppliers' reliability, understanding geopolitical risks, and considering the impact of seasonal or environmental factors. For example, traffic and gas prices might increase in summer months contributing to potential delays and higher costs.
Once you’ve identified the risks, develop strategies to lessen them. This might include diversifying your supplier base, holding safety stock, and creating contingency plans for emergencies.
- Strategies for Resilient Supply Chains:
Building a resilient supply chain means being prepared for disruptions and having plans in place to maintain operations. Strategies for resilience include:
-
- Diversification: Use multiple suppliers and transport routes to reduce dependency on any single source.
- Flexibility: Implement flexible contracts and production systems that can quickly adapt to changes.
- Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with all parts of your supply chain to quickly address and resolve issues.
- Technology: Use technology to enhance visibility and coordination across the supply chain.
By understanding and managing your supply chain effectively, you can ensure that your products reach your customers smoothly and efficiently, even in the face of challenges and changes.
For example, your supply chain might be very simple in the early stages of your business. If you have a graphic design business your supply chain might just consist of you providing services and sending emails with the amount due when the work is completed. As you grow, you may look at your supply chain for ways to be more efficient. For example, you might decide to adopt bookkeeping software to help you prepare project quotes, send invoices, and track income and expenses.
In the next sections, we’ll continue to explore more key aspects of business operations to help your small business thrive.
Developing a Sales Strategy
In this section, we'll focus on developing a sales strategy tailored to your small business needs. We'll briefly touch on sales goals and objectives, sales processes and methodologies, as well as fundamental marketing concepts. Additionally, we'll discuss the role of digital marketing and ecommerce strategies in supporting your sales efforts.
For more information on these topics, see our sessions on Marketing, Advanced Digital Marketing, Ecommerce, and Selling.
Sales Goals and Objectives
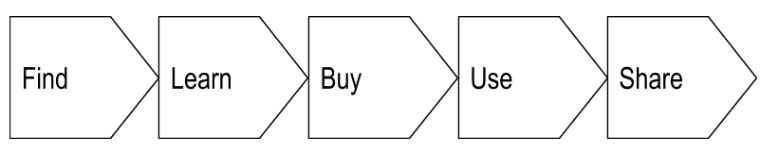
Setting clear sales goals and objectives is essential for guiding your sales efforts and measuring success. Determine specific targets for revenue, customer acquisition (getting new customers), and market share. Break down these goals into smaller, actionable steps to track progress and adjust strategies as needed. In MOBI’s Selling session, we discuss the five steps of the sales process in greater detail: Find, Learn, Buy, Use, and Share.
Sales Processes and Methodologies
Establishing effective sales processes and methodologies ensures consistency and efficiency in your sales efforts. Define the steps involved in prospecting, qualifying leads, making presentations, handling objections, and closing deals. Train your sales team on these processes and provide them with the tools and resources they need to succeed.
Marketing Fundamentals
While other MOBI sessions cover marketing strategies and techniques, it's important to understand the fundamentals. Conduct market research to identify your target audience, understand their needs and preferences, and assess your competition. Consider the “seven Ps of marketing” (Product, Price, Promotion, Place, Packaging, Positioning, and People) to develop strategies that effectively position your offerings in the market.
Digital Marketing and Ecommerce
In today's digital age, leveraging digital tools is essential for reaching your target audience and driving sales. Explore various digital marketing channels such as social media, email marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), and pay-per-click (PPC) advertising. Additionally, consider ecommerce strategies to expand your reach and facilitate online sales, such as building a user-friendly website, optimizing for mobile devices, and implementing secure online payment options for your customers.
By developing a comprehensive sales strategy that aligns with your business goals and incorporates digital marketing and ecommerce strategies, you can effectively drive sales and grow your small business.
Customer Experience and Feedback
The experience customers have with your business begins when potential customers first become aware of you, your product or your service, and ideally continues long after a purchase has been made. Business operations related to customer experience, customer service, and customer feedback also contribute to the success of your business. Visit the MOBI session on Customer Experience and Feedback to learn more about the components and factors that are part of this important area of your business and how to design processes to best encourage customer retention and loyalty.
In this section, we'll delve into the intricacies of managing costs, devising effective pricing strategies, and maintaining operational efficiency to ensure profitability. We'll reference concepts from finance, accounting, and cash flow management modules while focusing on exploring diverse pricing strategies, managing operational expenses, and assessing pricing for optimal financial outcomes.
(Reference MOBI's Financing the Business, Accounting and Cash Flow, and Controlling Costs sessions for more information.)
Factors Influencing Pricing
Several factors influence pricing decisions, including:
- Production Costs: Consider labor, materials, overheads, and other expenses incurred in manufacturing or delivering your product/service.
- Market Demand: Understand customer preferences, purchasing power, and trends to align prices with market dynamics.
- Competition: Analyze competitors' pricing strategies, product offerings, and value propositions to position your prices effectively.
- Perceived Value: Assess the value your product or service provides to customers and price accordingly to capture that value.
Pricing Strategies: Exploring Diverse Approaches
Pricing is a critical aspect of your business strategy, impacting revenue, market positioning, and customer perceptions. Let's delve into various pricing strategies to help you make informed decisions:
- Cost-Plus Pricing: This method involves calculating the total production cost and adding a markup to determine the selling price. While straightforward, it may overlook market demand and competition.
- Value-Based Pricing: This approach determines prices based on the perceived value of your product or service to the customer. It considers factors such as benefits, quality, and uniqueness, allowing you to capture value while remaining competitive.
- Penetration Pricing: Under this strategy, you set initial prices lower than competitors to penetrate the market rapidly. Once established, you may gradually increase prices. This approach is useful for gaining market share quickly but requires careful planning to avoid long-term profitability or customer experience issues.
- Competitive Pricing: In this model, prices are set based on competitors' prices. It requires continuous monitoring of competitors' pricing strategies and flexibility to adjust prices accordingly.
- Psychological Pricing: Setting prices to influence customers' perceptions, such as setting prices at $9.99 instead of $10 to make it seem cheaper.
- Dynamic Pricing: Adjusting prices based on market demand, competitor pricing, or other factors in real-time.
- Bundle Pricing: Offering multiple products or services together at a reduced price compared to purchasing them separately.
- Promotional Pricing: Temporarily reducing prices to stimulate sales or attract customers, often used during sales events or promotions.
Managing Operational Costs
As stated at the beginning of this session, business operations touch every aspect of your business. However, when we talk about “operational costs” we specifically mean the costs associated with running your business. Identifying and managing operational costs is crucial for achieving and maintaining profitability. If you don’t know how much it costs to deliver your product or service, you also won’t know whether or not you are making a profit. Major cost drivers include labor, materials, utilities, and overhead expenses. Many new business owners may focus only on the materials needed to create a product or service, especially if they are a solopreneur doing everything themselves. Strategies for cost management include:
- Identify ALL Costs: Understand your full product or service development process and make a list of all costs, even things that are hard to quantify like your time, utilities, and overhead.
- Streamlining Processes: Identify inefficiencies and optimize workflows to reduce waste and improve productivity.
- Supplier Negotiation: Negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, including bulk discounts, early payment discounts, and favorable payment terms.
- Technology Investment: Leverage technology to automate tasks, enhance efficiency, and reduce manual labor costs.
Evaluating Your Costs and Pricing
Regularly assess your costs and pricing strategy to ensure alignment with business objectives and market conditions. Monitor changes in costs for your supplies, market conditions, sales performance, customer feedback, and competitor pricing. Conduct profitability analysis to evaluate the impact of pricing decisions on your bottom line.
For example, an entrepreneur who had a home cleaning business wanted to expand to a neighboring town. After evaluating the cost of supplies, gas, time involved in scheduling, cleaning, and invoicing, the entrepreneur realized they were currently losing money on the service they were providing. They decided to increase their price and expand only within the current town, to reduce travel time and additional gas expenses.
By exploring diverse pricing strategies, managing operational costs effectively, and conducting regular pricing evaluations, you can increase profit and enhance the financial health of your business.
In this section, we'll delve into the crucial aspects of efficiency and quality management within business operations. We'll explore tools for quality management and strategies for enhancing operational efficiency through continuous improvement processes.
Establishing and Maintaining Quality in Your Business
Quality is one of the most important characteristics you will establish for your product or service. Quality can translate to perceived value, customer loyalty, price, profitability, and more. Similarly, inconsistent or poor quality can damage perceived value, customer loyalty, price, profitability, and more.
As a business owner, you will establish a quality assurance (QA) plan to ensure you maintain a consistent level of quality for your product or service by identifying key processes and areas where quality is critical, and then setting a standard that must always be met. You can then monitor and measure performance and outcomes against this standard in order to manage quality.
The business operations associated with maintaining quality are known as Quality Management Systems (QMS). QMSs are frameworks that help businesses maintain consistency and excellence in their products or services. These systems encompass policies, procedures, and processes designed to ensure that products or services meet specified quality standards and customer expectations.
Tools for Quality Management
Numerous tools and methodologies support quality management efforts, including:
- Checklists: Used to ensure that all necessary steps are followed in a process or task.
- Quality Control Charts: Graphical representations of quality data over time, helping identify trends and irregularities.
- Root Cause Analysis: A problem-solving technique used to identify the underlying causes of quality issues.
- Six Sigma: A methodology focused on process improvement and reducing defects or errors by tracking the number of errors and using statistics to measure this frequency.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): A contract between a business that provides a service and the customer of that service that outlines the level of service the customer can expect. It can be helpful for businesses to identify the service levels they will provide to their customers. As a simple example, your website or voicemail might include information telling customers that you will respond within 24 hours.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Continuous Improvement Processes
Continuous improvement involves regularly evaluating processes and implementing very small, or incremental changes to enhance efficiency and quality. This can include:
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review processes, procedures, and performance metrics to identify areas for improvement.
- Employee Involvement: Encourage employees to contribute ideas for process improvement and empower them to implement changes.
- Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms for collecting feedback from customers, employees, and stakeholders to identify opportunities for improvement.
By implementing Quality Management Systems, utilizing tools for quality management, and embracing continuous improvement processes, small businesses can enhance operational efficiency, improve product or service quality, and drive long-term success.
As you have now learned, operations exist in nearly all aspects of your business. They are the everyday activities that keep your business going. It’s important to recognize and record the operations that support and drive your business. This can be as simple as writing down the activities you undertake for each different function, whether supply chain, production, sales, marketing, or customer service. With this first step, you can begin to develop your operations plan, an important tool for evaluating the efficiency of your business.
Your operations plan can help you identify areas where you can be more efficient in order to increase customer satisfaction, profitability, and success. Your operations plan can be a blueprint for processes that can be easily adopted and implemented by other members of your team as your business grows. Operations can also help ensure the quality of your product or service is consistent, from one day, month, or year to the next, translating to customer satisfaction, loyalty, and trust.
THE TOP 10 DO'S
- Understand that business operations encompass the everyday activities necessary for running your business smoothly and efficiently.
- Utilize operations to ensure everyone works towards common goals.
- Align your operations with your business objectives to ensure that daily activities contribute to long-term goals.
- Prioritize customer needs and wants when designing and developing your offering, and focus on making your product easy to use, reliable, and cost-effective to produce.
- Establish efficient manufacturing processes that minimize waste and maintain consistent quality.
- Design a supply chain strategy that is efficient, flexible, and capable of responding quickly to changes in demand.
- Establish effective sales processes and methodologies to ensure consistency and efficiency in your sales efforts.
- Identify and manage operational costs effectively through strategies like streamlining processes, supplier negotiation, and technology investment.
- Regularly evaluate your pricing strategy to ensure alignment with business objectives and market conditions, monitoring sales performance, customer feedback, and competitor pricing.
- Use tools like checklists, charts, and analysis to manage quality effectively.
THE TOP 10 DON'TS
- Overlook the significance of quality control and efficiency in attracting customers and building customer loyalty.
- Neglect the role of operations in strategic planning; it's crucial for setting realistic goals and achieving long-term success.
- Skip operational planning because it seems difficult. It’s easy to start by documenting the processes you follow in running the different aspects of your business.
- Forget that good supply chain management will help you cut costs, maintain a consistent schedule, and keep your customers happy.
- Underestimate the impact of sustainability on brand image and customer loyalty.
- Develop your marketing strategies without first conducting market research to better understand your target audience.
- Make pricing decisions without considering factors such as production costs, market demand, competition, and perceived value.
- Evaluate and project your business’s profitability and financial health without including operational costs..
- Assume your operations plans will last forever, always evaluate the potential of emerging technologies to reshape the landscape of operations and create new opportunities for business growth and efficiency.
- Ignore ways to reduce waste and improve processes.
If you are currently writing or have developed a business plan, consider taking a moment now to include any information about your business related to this session. As a reminder, MOBI’s free Business Plan Template and any worksheets, checklists, and templates from this course are available for you to download. Just visit the list of MOBI Resource Documents on the Resources & Tools page of our website.