Exploring AI2 in Student Learning in Engineering
The following flowchart outlines the major steps you may take to explore AI2 in student learning. Below the flowchart are resources that you may find useful when going through each step in the flow chart. (Text only version of the flowchart available here.)
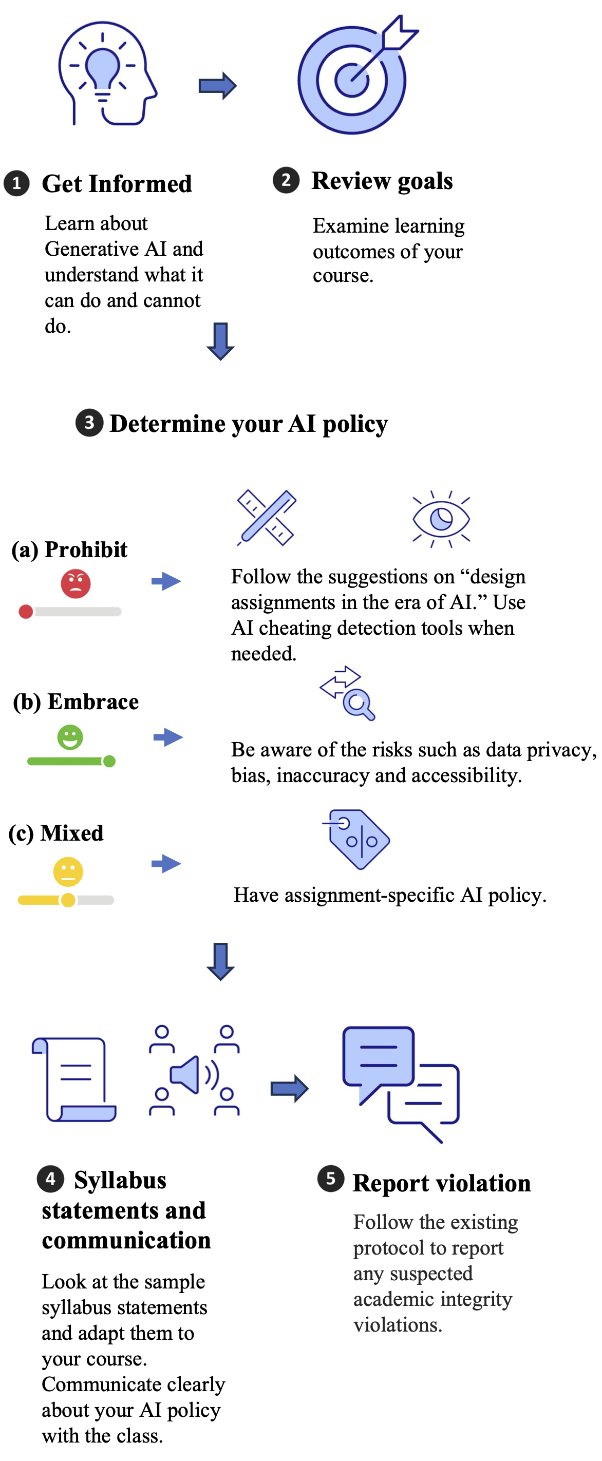
1. Getting Informed about Generative AI
See a list of FAQs about generative AI and its use in higher education.
2. Reviewing Learning Goals of Your Course
To begin with, think about whether the use of generative AI tools in your course would support the learning goals of your course. This may help you determine whether or when to allow students to use the tools. It is important to examine the learning outcomes of your courses and adopt a suitable AI policy, since learning outcomes are what students should know and be able to do by the end of the course. Please see below some related resources at SCU and other institutions:
In particular, Bloom's taxonomy is often a good starting point when thinking about learning outcomes.
Here is another article on How Teachers Can Use Bloom’s Taxonomy with ChatGPT: Practical Classroom Strategies
3. Determining Your AI Policy: Resources
The figure extracted from the document "ChatGPT and AI in higher education" from the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Culture Organization (UNESCO), lists different roles generative AI tools could play in higher education.
Preface:
Currently, looking at all the “free” and “paid” AI detectors, there are none that are highly recommended in industry with a high accuracy rate. Many of them struggle with high rate detection on a material that is human written and struggle to detect AI written. ChatGPT can now be queried to re-write its output style to more closely match human written than AI.
Ways to circumvent many of the detector tools:
- Reword key words and phrases. You can ask AI to rewrite certain passages as well to change style to be less AI written.
- Many of these tools are not geared toward “coding” snippets. However, to circumvent detection would be to replace variable names and values to less popular terms. Something that is very easy to do. There currently isn’t any tool that I found that is geared towards detecting written code. Most of them claim to work but fail to have any reputable results.
While these tools can be used, the issue will be trusting their result accuracy. It might take using two or more tools in conjunction to further increase result accuracy. Many of the tools do have a “free” limit and may exceed your usage needs.
Popular AI Detectors
Some AI detectors have a high failure rate based on reviewers and commentators from various sources. With those AI detectors eliminated, below is a list of popular AI detectors,
- Writer.com: Free
- ContentAtScale: Free
- Grammica: Free, with lots of ads.
- CopyLeaks: Free, sign up required
- GPTkit.ai: First 2048 characters in every request will be free
- Sapling: Free for 3 (snippets). Requires subscription
- Winston.AI: Free up to 2000 words, sign up required
- ZeroGPT: Free up to 15,000 characters, paid subscription for expanded features
- GPTZero : Free up to 5000 characters, then paid subscription after
- Originality.ai Paid - $15 per month or $30 pay as you go
- Turnitin : Newly launched but requires paid subscription
Out of the list, AI detectors that have reputation for having the most accurate results (please see Preface) are
- GPTZero : Free up to 5000 characters, then paid subscription after
- Originality.ai Paid - $15 per month or $30 pay as you go.
- Having students complete assignments and exams during class (in person).
- Asking more nuanced questions that may be beyond the capabilities of the current AI tools.
- Requiring students to show intermediate results of their assignments or projects before they submit their finished work.
- Supplementing written assignments with additional oral presentations, flowcharts, concept maps, group work, case studies, etc.
- Data Privacy and Security: Entering data into ChatGPT is like posting that data on a public website. You may not enter internal, sensitive or restricted data into any generative AI tool or service.
- Inaccuracies and Misinformation: Generative AI has the potential to generate responses that may not always be accurate or up-to-date. It is advisable for users to independently verify information obtained from generative AI, particularly when dealing with specific facts or fast evolving subjects.
- Bias and Unintentional Harm: Generative AI may inadvertently mirror biases present in its training data. It is important to critically assess and place into context the responses generated by generative AI to ensure equitable and unbiased dissemination of information.
- Inappropriate Content: Despite efforts by generative AI providers to filter out inappropriate content, there remains a possibility that generative AI may produce or respond to content that is offensive, inappropriate, or breaches ethical standards.
- SCU Library’s libguide, which also includes the pledge (not an honor code)
- Teaching Academic Integrity, A digital resource about AI
- AI in the classroom
Bioengineering
- ChatGPT can reshape medical education and clinical management according to Khan et al. “Khan RA, Jawaid M, Khan AR, Sajjad M. ChatGPT - Reshaping medical education and clinical management. Pak J Med Sci. 2023 Mar-Apr;39(2):605-607”
- Some of the ways ChatGPT can help in medical education are
- Automated Scoring: ChatGPT can be effectively used to assess student papers and essays and analyze the sentence structure, vocabulary, grammar, and clarity of a paper.
- Teaching Assistance: Another use of ChatGPT is its ability to generate exercises, quizzes and scenarios that can be used in the classroom to help practice and assess.
- Personalized Learning: ChatGPT can be used to create virtual tutors or assistants that can answer students’ questions as well as provide feedback on their work.
- Research Assistance: ChatGPT can also be utilized to assist students in their research by answering questions and providing summaries of texts.
- Quick Access to information: ChatGPT can be utilized to provide accurate and up to date information on medical topics at a moment’s notice.
- Generating Case Scenarios: ChatGPT can be used to generate case studies and scenarios to help medical students practice and improve their diagnostic and treatment planning abilities.
- Creating Content to Facilitate Learning: Another function that ChatGPT provides is its ability to create content for summaries, quizzes, and flashcards.
- Language Translation: ChatGPT’s ability to translate language effectively can be utilized by medical professionals and educators to help communicate with patients from different linguistic backgrounds, in order to provide the best medical care."
- ChatGPT can help with the capstone projects for
- Suggesting experimental techniques
- Suggesting mathematical models
- Writing introduction
- Analyzing results
- Lo et al. “Lo, Po Sang and Yeoh, Keat Ping, Efficient Utilization of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Capstone Projects. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4435145 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4435145” describes a step by step approach to facilitate effective communication with chatGPT:
- Assign a role to ChatGPT; this can allow it to focus deeper on a specific expertise area, providing additional insights and information that may not be readily available through other sources.
- Be clear and concise when asking questions. This will maximize the response from chatbot
- Provide context to questions. This will help ChatGPT better understand what is being asked.
- Using specific keywords related to the capstone project when asking questions. This can help ChatGPT provide more relevant and accurate responses.
- Ask follow-up questions. This can aid in obtaining more information or clarification.
Civil, Environmental and Sustainable Engineering
- This article includes interesting examples (for lower and upper division courses) using ChatGPT for teaching
- Interesting article: Engineering Education in the Era of ChatGPT: Promise and Pitfalls of Generative AI for Education
- This article focuses on AI for civil engineering education
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO): ChatGPT and AI in higher education
- ChatGPT and civil engineering calculations example
- Where will AI like ChatGPT take civil engineering in the future?
- Ultimate Guide to ChatGPT for Engineers
- 10 Ways To Use ChatGPT To Write Research Papers (ETHICALLY) In 2023
- Investigating the Use of ChatGPT for the Scheduling of Construction Projects
- Leveraging ChatGPT to Aid Construction Hazard Recognition and Support Safety Education and Training
Computer Science and Engineering
- ChatGPT in Computer Science Education: Freshmen's Perceptions
- Recommendations to Create Programming Exercises to Overcome ChatGPT
- ChatGPT in Computer Science Education
- ChatGPT Participates in a Computer Science Exam
- On the educational impact of ChatGPT: Is Artificial Intelligence ready to obtain a university degree?
- ChatGPT for Teaching and Learning: An Experience from Data Science Education
Electrical and Computer Engineering
- ECE Summit: What is the Role of ChatGPT in ECE? How will Generative AI Drive Innovation?
- MATLAB and ChatGPT
- Verilog HDL and ChatGPT
- Python and ChatGPT
Mechanical Engineering
- The Possibility of Applying ChatGPT (AI) for Calculations in Mechanical Engineering
- Using ChatGPT as a Mechanical or Aerospace Engineer
- ChatGPT for Different Engineering Problems
General Resources and Discussions
- "Instead of Policing Students, We Need to Abolish Cheating - the best response to ChatGPT is to pay more attention to why students cheat in the first place", by Jordan Alexander Stein, September 7, 2023, the Chronicle of Higher Ed.
- "How AI Could Save (Not Destroy) Education", by Sal Khan, the founder and CEO of Khan Academy, TED Talk, May 1, 2023.
4. Sample Syllabus Statements
We understand that a "one-size-fits-all" approach to syllabus statements is not suitable since each discipline and course has its own unique goals and learning outcomes. SCU's Academic Integrity policy underscores the importance of each instructor's responsibility to clearly communicate our own policies in the syllabus. Regardless your approach to the use of AI tools, be as specific as possible in addressing questions such as:
- Under what circumstances are generative AI tools allowed?
- What is the rationale or justification behind this policy?
- What are the consequences for students violating the course policy?
- What are other forms of assistance and collaborative efforts acceptable? Identify the assignments for which such assistance is permitted.
- Where and how should students disclose their use of AI?
Below, you can find practical examples of syllabi statements that address various scenarios and disciplines. This list is not exhaustive, but we hope it can serve as a starting point for you to create your own statement. You are encouraged to either adopt the provided examples or adapt it to fit your particular needs.
Instructors may consider different possible scenarios below and adapt the sample statements for their own courses:
- Prohibited in all circumstances
Since basic writing, analytical, critical thinking skills are part of the learning outcomes of this course, use of ChatGPT (or other similar generative AI tools or software) is not allowed in this class for any part of a graded assignment, including generation of ideas, writing of text, rewriting your own work, or generating computer code. Doing so is considered a violation of SCU’s Academic Integrity and suspected use will be reported to the Office of Student Life. - Allowed for specific assignments, projects, or tasks
In this class, you are permitted to utilize ChatGPT or similar AI generation tools, but only for designated assignments. When the use of such tools is acceptable, it will be clearly indicated in the assignment instructions. If you choose to employ ChatGPT at any stage of the assignment, whether it is for brainstorming, text creation, editing, or computer coding, it is essential to provide proper attribution. Neglecting to cite the AI tool will be regarded as a breach of the Academic Integrity policy and plagiarism standards. - Allowed with prior permission
If you intend to employ ChatGPT or similar generative AI tools for any part of the assignments, including idea generation, text composition, text editing, or computer programming, it is necessary to request permission first and provide a clear description of your intended usage. Furthermore, proper attribution to ChatGPT must be ensured in your assignment submission. - Allowed with attribution
Students in this course are allowed to utilize AI tools, such as ChatGPT, if they so choose. To align with our academic principles, it is mandatory for students to provide citations for any AI-generated content that contributed to their work. This citation requirement encompasses in-text citations, the use of quotations, and inclusion in the reference list. Failing to attribute AI-generated content appropriately constitutes a breach of academic integrity.
BIOE 174 Microfabrication and Microfluidics for Bioengineering Applications
You are welcome/expected to use generative AI tools (e.g., ChatGPT etc.) in this class as doing so aligns with the course learning goals (i.e., explain microfabrication techniques and microfluidics technologies, designing creative devices for biomedical applications, etc.). You are responsible for the information you submit based on an AI query (for instance, that it does not violate intellectual property laws, or contain misinformation or unethical content). Your use of AI tools must be properly documented and cited in order to stay within university policies academic honesty.
CENG 41 Statics - Undergraduate (Prohibited use)
In this course, the use of generative AI tools, including but not limited to ChatGPT, GPT-4, CoPilot, and similar technologies, is strictly prohibited. Generative AI tools have the capability to automatically generate code, solutions, or other content, which directly conflicts with the core principles of this course. The trust and integrity of the learning process, as well as the assessment of individual student understanding, are paramount. Using generative AI tools to produce solutions or content for assignments, projects, exams, or any other course-related tasks is considered a violation of academic integrity. The goal of this course is to foster your independent thinking, problem-solving skills, and understanding of statics principles. Relying on AI-generated content undermines these objectives and unfairly advantages some students over others. It is essential that all assignments and assessments you submit in this course are a genuine representation of your own individual efforts and understanding. Collaboration and discussion with your peers and instructors are encouraged as part of the learning process. However, the use of generative AI tools crosses the boundary of acceptable collaboration and is not conducive to your academic growth.
Any violations of this policy will be treated seriously and in accordance with the SCU academic integrity standards. As responsible and ethical engineers-in-training, it is crucial to uphold the principles of integrity, honesty, and individual effort throughout your educational journey. If you have any questions about the use of specific tools, technologies, or resources, please consult the course instructor for clarification before proceeding. Your commitment to academic integrity and adherence to these guidelines will contribute to a fair, respectful, and productive learning environment for all students.
CENG 43 Strength of materials - Undergraduate (Allowed Use of Generative AI with Prior Permission)
In this course, we acknowledge the potential of generative AI tools to contribute to the exploration of complex structural problems and analysis. Generative AI, including tools like ChatGPT, GPT-4, CoPilot, and similar technologies, can offer innovative perspectives to address design challenges. To ensure the responsible and meaningful integration of these tools, we have established specific guidelines for their use within this course.
Requesting Permission to Use Generative AI:
Students may request prior permission to utilize generative AI tools for specific problems assigned in this course. These requests should be submitted to the course instructor, detailing the problem and the intended use of the AI tool. Permission will be granted on a case-by-case basis, and only for designated assignments. This approach ensures that generative AI tools are used thoughtfully and in alignment with the learning objectives.
Comparing Solutions with Class Lectures:
If granted permission, students are required to compare the solutions generated by generative AI tools with the solutions discussed during class lectures. This comparison serves as an important step to critically assess the output of generative AI. It enables you to identify the current limitations of these tools, as well as to recognize their potential benefits in the context of strength of materials analysis.
Understanding AI Limitations:
Generative AI tools, while powerful, have inherent limitations that stem from their training data and algorithms. By comparing the AI-generated solutions with those derived from class lectures, you will gain valuable insights into the accuracy, feasibility, and applicability of generative AI within the field of strength of materials.
Promoting Responsible Use and Learning:
The purpose of allowing generative AI use with prior permission is to encourage responsible experimentation and exploration. This approach facilitates a deeper understanding of the capabilities and challenges associated with AI technologies. By critically evaluating and comparing solutions, you will develop a nuanced perspective on the role of generative AI in engineering problem-solving.
CENG 135 Reinforced concrete design - Undergraduate (Allowed for specific assignments, projects, or tasks)
In this course, there are specific instances where the use of generative AI tools will be allowed for assignments and projects. Generative AI, including tools like ChatGPT, GPT-4, CoPilot, and similar technologies, can offer innovative ways to approach complex design challenges. However, its use must be carefully controlled and ethically managed to ensure a fair and transparent learning environment.
Use of Generative AI for the final course project and intermediate deliverables:
For the course project and its intermediate deliverables, students are permitted to utilize generative AI tools to assist in the design process. This allowance is provided to encourage exploration and creativity in your design work. When using generative AI for these components, you must clearly cite and explain its application in your project documentation. This will demonstrate your understanding of how the technology contributed to your design decisions and solutions.
Citing and Explaining Generative AI Usage:
When incorporating generative AI into your project and intermediate deliverables, it is essential to provide clear citations for the AI-generated content you use. Additionally, your documentation should explain how the generative AI contributed to your design choices and outcomes. This practice ensures transparency and accountability in your work, highlighting the collaborative synergy between human creativity and technological innovation.
Generative AI Use for Weekly Assignments:
Conversely, the use of generative AI tools is not permitted for weekly assignments. The purpose of weekly assignments is to assess your individual understanding of the course material, problem-solving skills, and analysis capabilities. Using generative AI for these assignments contradicts the objectives of assessing your personal learning and may lead to an unfair advantage over your peers.
Academic Integrity and Collaboration:
While generative AI tools are permitted for specific components of this course, it is important to uphold the principles of SCU academic integrity and responsible collaboration. Utilize generative AI as a supplementary tool to enhance your design process, rather than relying solely on its output. Maintaining a balance between your individual insight and AI assistance will contribute to your growth as an engineer and ethical professional.
Any instances of misusing or misrepresenting generative AI tools, including failing to provide proper citations or explanations, will be considered a violation of the SCU code of academic integrity. Consequences for such violations will be consistent with the policies set by this institution.
If you have any questions about the appropriate use of generative AI tools or need guidance on how to cite and integrate them into your project, please consult the course instructor before proceeding.
CENG 220 Structural dynamics - Undergraduate (Allowed Use of Generative AI with Attribution)
In this course, we recognize the potential benefits that generative AI tools can offer to enhance the analysis and understanding of complex structural dynamics. Generative AI, including tools such as ChatGPT, GPT-4, CoPilot, and similar technologies, can provide innovative insights and solutions that complement your learning experience. To ensure the responsible and meaningful integration of these tools, we have established specific guidelines for their use within this course.
Utilizing Generative AI with Attribution:
You are allowed to utilize generative AI tools for assignments, projects, or tasks within this course. When incorporating content generated by these tools into your work, you are required to provide proper attribution to the source of the AI-generated content. Proper attribution acknowledges the contribution of generative AI while maintaining transparency in your work.
Guidelines for Attribution:
When using generative AI-generated content, ensure that you:
- Clearly identify and distinguish the content generated by the AI tool.
- Provide a citation or reference to the AI tool used (e.g., "Generated using ChatGPT, a language generation AI tool").
- Specify the role of the generative AI content in your work, explaining how it contributes to your analysis, insights, or solutions.
Academic Integrity and Responsible Use:
While the incorporation of generative AI content is permitted in this course, it is crucial to maintain SCU’s academic integrity standards and responsible use. The use of generative AI should enhance your understanding and facilitate your learning journey. Plagiarism, misrepresentation, or unethical use of generative AI-generated content will not be tolerated and will be addressed according to SCU’s academic integrity policies.
Consultation and Clarity:
If you have any uncertainties or questions regarding the appropriate use of generative AI tools, citation practices, or attribution guidelines, please do not hesitate to seek guidance from the course instructor.
COEN 11 Advanced Programming
(Prohibited in all circumstances)
Since gaining basic programming skills are part of the learning outcomes of this course, all assignments should be prepared by the student. Developing strong competencies in this area will prepare you for a competitive workplace. Therefore, code generation tools (AI-based or otherwise), such as ChatGPT, GPT4, CoPilot, are strictly prohibited in this course, even when properly attributed. The use of such tools is considered a violation of SCU’s Academic Integrity and suspected use will be reported to the Office of Student Life.
COEN 346 Natural Language Processing
(Allowed with attribution)
You are welcome and expected to use generative AI tools (e.g. ChatGPT, GPT-4, etc.) in this class as doing so aligns with the course learning goal including understanding the capabilities and limitations of the state-of-art technologies in natural language processing. You are responsible for the information you submit based on an AI prompt (for instance it does not violate data privacy, intellectual property laws, or contain misinformation or unethical content). Proper attribution and a clear description of how you incorporated their input into your work is required. Here are some instructions.
ELEN/COEN 21 Intro to Logic Design
(Allowed for specific assignments, projects, or tasks)
Use of ChatGPT (or other similar tools that generate text) is allowed in this class for specific assignments only. When use of the tool is allowed, it will be explicitly noted in the assignment directions. If you utilize ChatGPT for any part of the assignment (from idea generation to text creation to text editing), you must properly cite ChatGPT. Failure to cite ChatGPT is considered a violation of the plagiarism standard of the Academic Integrity. Violations could result in failure of the assignment or failure of the course.
You will be assigned design problems that compare the solutions based on the class lectures with the solutions provided by ChatGPT. This comparison will enable the students to clearly see the current limitations of using ChatGPT.
Example: Explain how a logic decoder works.
Example: Explain how a 4:1 multiplexer works.
Example: How to design logic for a simple calculator ?
Code generation tools (AI-based or otherwise), such as ChatGPT, GPT4, CoPilot, etc. for generating Verilog Hardware Description Language (HDL) code will be explored.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OoI2eHeK3Og
Example: Write Verilog code for a 2-input 16-bit adder.
ELEN 520 Machine Learning (Free to use with attribution)
You are free to discuss the homework assignments with other students and work towards solutions together. However, all of the code (Python) you claim to write must be your own. In addition, your writeup must be entirely your own. Furthermore, for the purposes of this course, we will consider language modeling-based assistants like ChatGPT and GPT-4 in the same vein as other external resources or collaborators. You are free to use them, but you may not claim the content produced from these assistants as your own. You may quote them with appropriate attribution and describe how you used them in your writeup.
MECH 121 Thermodynamics
In this class, we consider AI-based assistance (e.g., ChatGPT and GPT-4) the same way we treat interaction with other people. You are welcome to discuss homework assignments with other people as well as with AI-based assistants. However, any work you submit must be your own. We suggest the following practice to avoid crossing the line into academic misconduct: You can interact with other people or AI-based assistants as a preparation before writing the assignments. After the interaction, turn off any AI-based assistance and write your assignments independently to reflect your revised knowledge.
MECH 294 Applied Machine Learning in Engineering and Design
(Allowed for specific assignments, projects, or tasks)
Types of things that are OK for problem sets, independent learning assignments (ILAs), and class projects:
- Asking ChatGPT (or other similar Generative AI tools that generate text, equations, and codes) where in the readings things can be found or located.
- Asking Generative AIs to provide high-level, non-library, or code-level guidance, e.g., "I found the sklearn clustering page helpful," and " I found the shapenet dataset useful."
Types of things that are NOT OK for problem sets, independent learning assignments (ILAs), online quizzes, and class projects:
- Asking Generative AIs to answer the questions in the problem sets and online quizzes for you.
- Asking Generative AIs to generate the project report for you. e.g., generating a literature review section by ChatGPT without reading related works.
This list is not exhaustive; ask the instructor before using any Generative Al-based source not explicitly listed above. For the purpose of this course, students learn how to create machine learning models and implement them. To maximize the learning outcomes and avoid the violation of academic integrity, Generative AIs must be appropriately used for specific portions of the assignment, projects, or tasks. Using Generative AIs to generate content for improper portions in assignments, projects, or tasks qualifies as academic dishonesty.
5. Reporting Violations
Follow SCU’s existing protocol to report an academic integrity violation
- Faculty Information for Reporting a Violation
- Student Information for Reporting a Violation
This form is for reporting an academic integrity violation of the Student Conduct Code by a Santa Clara University student. Faculty and students are directed to use this form when reporting an academic integrity violation.